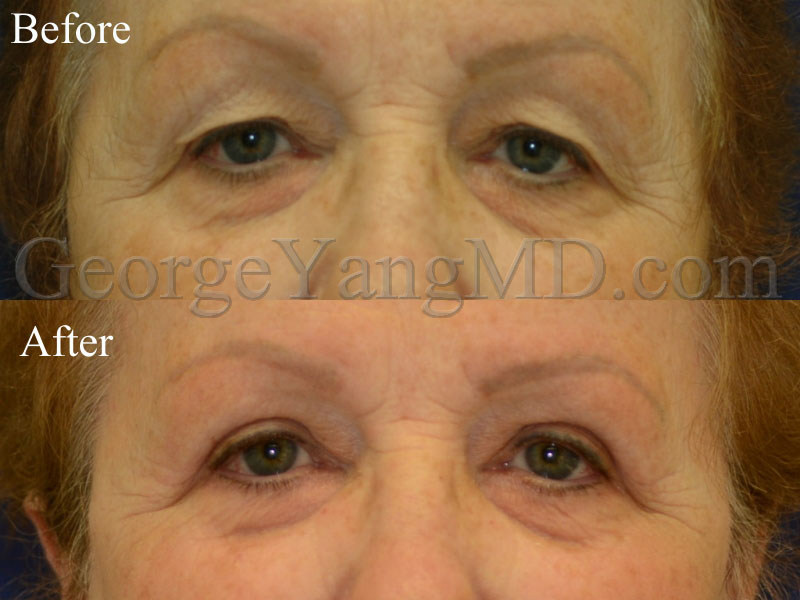
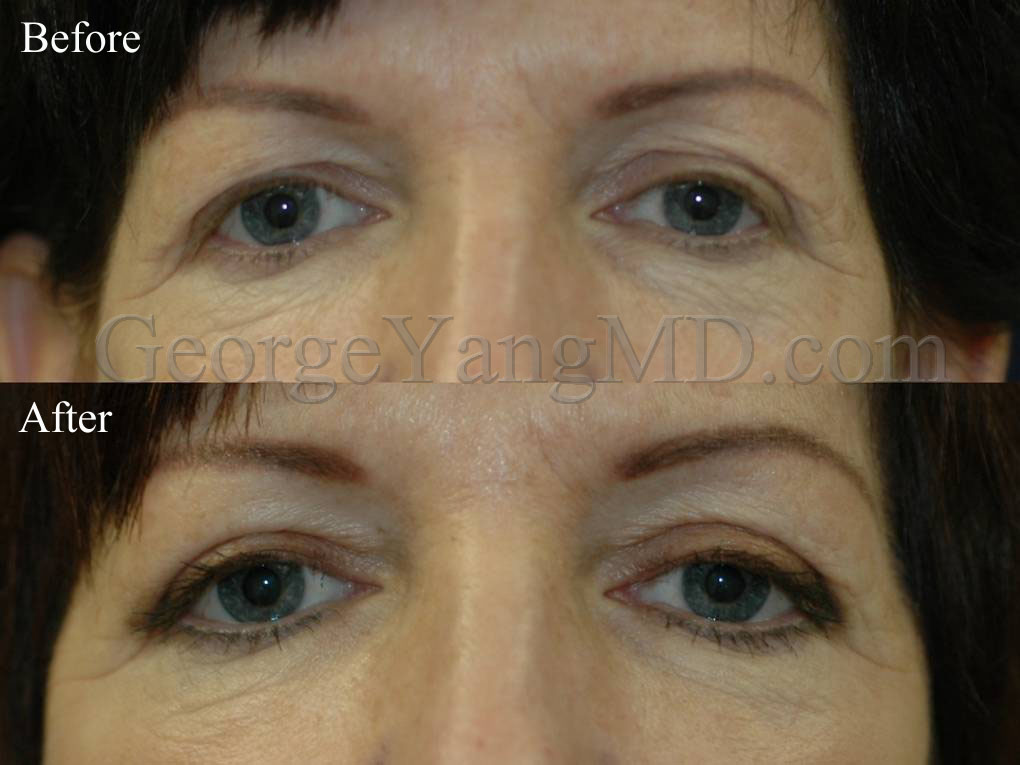
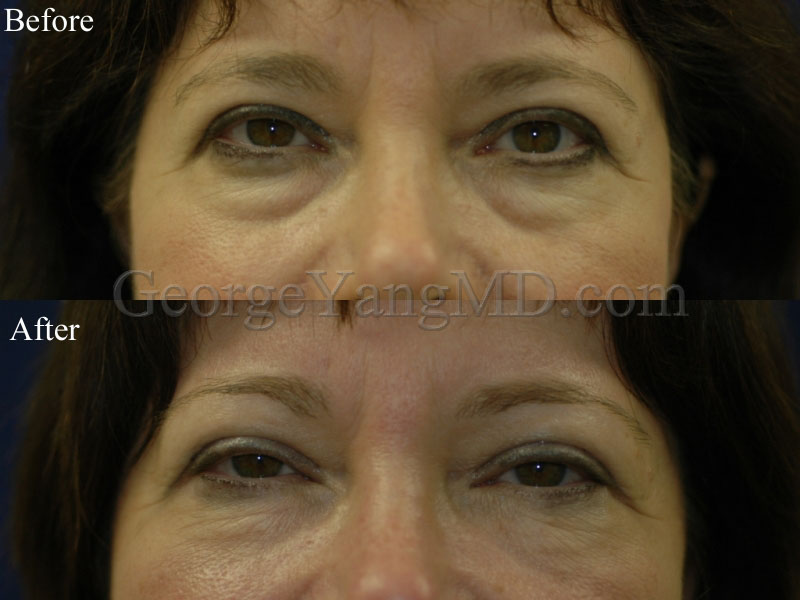
Eyelid Surgery or Blepharoplasty is a procedure to remove excess fat, sagging or wrinkled skin and sometimes muscle from the upper and/or lower eyelids. As the skin ages and sags, the upper eyelid can accumulate excess skin creating a “hooding” effect which is often aesthetically displeasing to patients and can even interfere with vision. The opposite seems to occur for volume in the lower eyelid area. As the area around the eyes age and volume is displaced, there is a movement of fat from under the eye in a diagonal fashion towards the cheek. This can result in dark circles, “puffy” lower eyelids, and eyebags.
Upper | Lower Blepharoplasty Candidate
Aging in the upper eyelid region is not uniform and varies greatly among patients. The Upper Blepharoplasty procedure is recommended for patients with upper eyelid hooding that results from excess eyelid skin. Wrinkling and excess upper eyelid skin appear as we age due to decreased skin elasticity and volume loss from the brow region. The hooding effect that occurs can cause vision impairment.
A Lower Blepharoplasty does not specifically treat wrinkling like an Upper Blepharoplasty, but removes excess fat that situates itself below the eye as we age. Dr. Yang performs him Lower Blepharoplasty procedure to reduce the appearance of lower eyebags and smooth the lower eyelid region.
About the Procedure
The intricacies of Dr. Yang’s Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty vary on each patient’s individual needs. However, for most patients Dr. Yang removes upper eyelid skin and fat via an incision along the crease of the eyelid.
During the Lower Eyelid Blepharoplasty (also known as Transconjunctival Blepharoplasty), Dr. Yang removes any excess fat via an incision along the inside of the eyelid rim (the pink inner lining of the lower eyelid) where stitches are not necessary. For patients requiring excess skin removal in the lower eyelid region, Dr. Yang removes excess skin and fat via an incision just below the patient’s eyelash line.
Dr. Yang performs the Upper and Lower Blepharoplasty in the office surgical suite under local anesthesia for most patients. In some cases where a patient may elect for general anesthesia or is combining the procedure with another, more invasive procedure, it may be performed at Manhattan Eye, Ear and Throat Hospital (part of Lenox Hill Hospital on the Upper East Side).
Recovery
Patients should expect some swelling from the procedure, but discomfort is minimal. Dr. Yang removes the stitches within seven to ten days of the surgery and most patients resume normal activities within two weeks.
Before and After Photos